Setting Breakpoints and Stepping through a Program
Action Points (breakpoints)
An action point is TotalView’s much more powerful version of a breakpoint. Here are the four types:
 Breakpoint
Breakpoint - stops execution of the processes or threads that reach it.
 Process Barrier Point
Process Barrier Point - holds each process when it reaches the barrier point until all processes in the group have reached the barrier point. Primarily for MPI programs.
 Evaluation Point
Evaluation Point - executes a code fragment when it is reached. Enables you to set “conditional breakpoints” and perform conditional execution.
 Watchpoint
Watchpoint - monitors a location in memory and either stops execution or evaluates an expression when the value stored in memory is modified.
Set action points in the Process Window with a single left-click on the line number. TotalView displays a

sign.
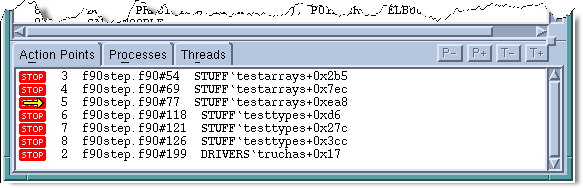
View all action points in the Process Window’s Action Points tab.
When your program halts on an action point, TotalView reports this status in various ways, including in the Root Window, the Process Window’s Source Pane, and through a yellow arrow (
Figure 12) on the Action Points tab.
Once you have created an action point, you can save, reload, suppress, and redefine its characteristics in a number of ways. You can set action points on all functions within a class or on a virtual function, and finely control how action points work in multi-threaded multi process programs.
See More

On the CLI command
dactions to display, save, and reload action points:
dactions in the
TotalView Reference Guide
On the role of barrier points in multi-threaded processes:
“Using Barrier Points” in the
TotalView User Guide