GPU Variable and Data Display
TotalView can display variables and data from a CUDA thread.
Add an expression from the Call Stack to the Data View to display parameter, register, local, and shared variables, as shown in Figure 122. The variables are contained within the lexical blocks in which they are defined. The type of the variable determines its storage kind (register, or local, shared, constant or global memory). The address is a PTX register name or an offset within the storage kind.
Figure 122, The Data View displaying a parameter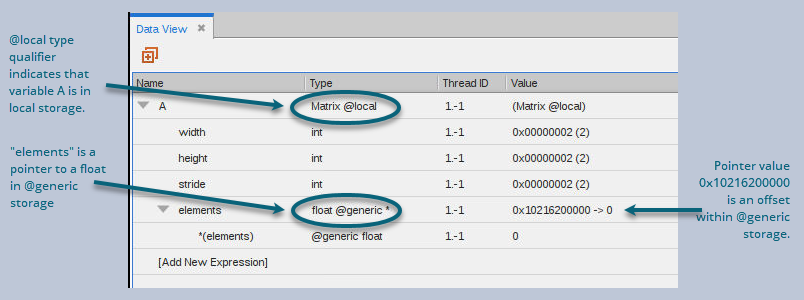

The identifier @local is a TotalView built-in type storage qualifier that tells the debugger the storage kind of "A" is local storage. The debugger uses the storage qualifier to determine how to locate A in device memory. The supported type storage qualifiers are shown in Table 13.
Storage Qualifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
@code | An offset within executable code storage |
@constant | An offset within constant storage |
@generic | An offset within generic storage |
@frame | An offset within frame storage |
@global | An offset within global storage |
@local | An offset within local storage |
@parameter | An offset within parameter storage |
@iparam | Input parameter |
@oparam | Output parameter |
@shared | An offset within shared storage |
@surface | An offset within surface storage |
@texsampler | An offset within texture sampler storage |
@texture | An offset within texture storage |
@rtvar | Built-in runtime variables (see CUDA Built-In Runtime Variables) |
@register | A PTX register name (see PTX Registers) |
@sregister | A PTX special register name (see PTX Registers) |
@managed_global | Statically allocated managed variable. See Managed Memory Variables. |
The type storage qualifier is a necessary part of the type for correct addressing in the debugger. When you edit a type or a type cast, make sure that you specify the correct type storage qualifier for the address offset.