TotalView can debug programs that run in many different computing environments using many different parallel processing modes and systems. This section looks at few of the ways you can start TotalView. See the “TotalView Command Syntax” chapter in the TotalView Reference Guide for more detailed information.
where executable is the name of the executable file to debug and corefiles is the name of one or more core files to examine.
|
Your environment may require you to start TotalView in another way. For example, if you are debugging an MPI program, you must invoke TotalView on mpirun. For details, see Chapter 7, “Setting Up Parallel Debugging Sessions”.
Note that you can use the GUI and the CLI at the same time. Use the Tools > Command Line command to display the CLI’s window.
Starting TotalView
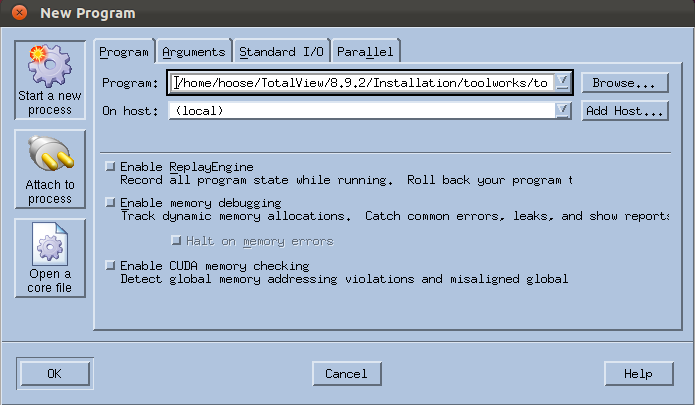
Starts TotalView without loading a program or core file. Instead, TotalView displays its File > New Program dialog box to enter information to load your program, Figure 51.
|
In the GUI, notice the checkboxes on the Program tab. These enable reverse debugging with ReplayEngine and memory debugging and notifications using MemoryScape to stop executing when memory events occur.
If you installed TotalView on a Macintosh using the application bundle, you can click on the TotalView icon. If you’ve installed the .dmg version, you can start TotalView from an xterm by typing:
installdir/TotalView.app/totalview
where installdir is where TotalView is installed.
If TotalView was installed on your system without procmod permission, you will not be able to debug programs. If TotalView detects this problem, it displays a dialog box with information on how to fix it.
Debugging a program
totalview executable
Starts TotalView and loads the executable program.
|
If you installed TotalView on a Macintosh using the application bundle, you can drag your program’s executable to the TotalView icon on your desktop.
If you type an executable name, TotalView remembers that name and many of its arguments.
Debugging a core file
totalview executable corefiles
|
The corefiles argument represents one or more core files associated with this executable. You can use wild cards in the core file name.
Passing arguments to the program being debugged
Starts TotalView and passes all the arguments following the –a option to the executable program. When using the –a option, it must be the last TotalView option on the command line.
|
If you don’t use the –a option and you want to add arguments after TotalView loads your program, add them either using the Arguments tab within the File > New Program dialog box or use the Process > Startup command.
Debugging a program that runs on another computer
Starts TotalView on your local host and the tvdsvr on a remote host. After TotalView begins executing, it loads the program specified by executable for remote debugging. You can specify a host name or a TCP/IP address. If you need to, you can also enter the TCP/IP port number.
|
If TotalView fails to automatically load a remote executable, you may need to disable autolaunching for this connection and manually start the tvdsvr. (Autolaunching is the process of automatically launching tvdsvr processes.) To disable autolaunching, add the hostname:portnumber suffix to the name entered in the Host field of the File > New Program dialog box. As always, the portnumber is the TCP/IP port number on which TotalView server is communicating with TotalView. See “Starting the TotalView Server Manually” for more information.
Debugging an MPI Program
(method 1) In many cases, you can start an MPI program in much the same way as you would start any other program. However, you need to select the Parallel tab within the File > New Programs dialog box, and the MPI version in addition to other options.
(method 2) The MPI mpirun command starts the TotalView executable pointed to by the TOTALVIEW environment variable. TotalView then starts your program. This program runs using count processes.
Using gnu_
debuglink Files
debuglink Files
If you have prepared a gnu_debuglink file, TotalView can access this information. For more information, see “Using gnu_debuglink Files” within the Compilers and Platforms chapter of the TotalView Reference Guide.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remote debugging, see Chapter 5, “Setting Up Remote Debugging Sessions” and “TotalView Debugger Server (tvdsvr) Command Syntax” in the TotalView Reference Guide.
|