The following paragraphs, which are copied from the Global Arrays home site (http://www.emsl.pnl.gov/docs/global/um/intro.html), describe the global arrays environment:
The Global Arrays (GA) toolkit provides a shared memory style programming environment in the context of distributed array data structures (called “global arrays”). From the user perspective, a global array can be used as if it was stored in shared memory. All details of the data distribution, addressing, and data access are encapsulated in the global array objects. Information about the actual data distribution and locality can be easily obtained and taken advantage of whenever data locality is important. The primary target architectures for which GA was developed are massively-parallel distributed-memory and scalable shared-memory systems.
GA divides logically shared data structures into “local” and “remote” portions. It recognizes variable data transfer costs required to access the data depending on the proximity attributes. A local portion of the shared memory is assumed to be faster to access and the remainder (remote portion) is considered slower to access. These differences do not hinder the ease-of-use since the library provides uniform access mechanisms for all the shared data regardless where the referenced data is located. In addition, any processes can access a local portion of the shared data directly/in-place like any other data in process local memory. Access to other portions of the shared data must be done through the GA library calls.
GA was designed to complement rather than substitute for the message-passing model, and it allows the user to combine shared-memory and message-passing styles of programming in the same program. GA inherits an execution environment from a message-passing library (w.r.t. processes, file descriptors etc.) that started the parallel program.
TotalView supports Global Arrays on the Intel IA-64 platform. Debug a Global Arrays program in basically the same way that you debug any other multi-process program. The one difference is that you use the Tools > Global Arrays command to display information about your global data.
|
|
|
|
Cast the data so that TotalView interprets data as a global array handle. This means that TotalView displays the information as a global array. Specifically, casting to $GA forces the Fortran interpretation; casting to $ga forces the C interpretation; and casting to $Ga uses the language in the current context.
|
Within a Variable Window, the commands that operate on a local array, such as slicing, filtering, obtaining statistics, and visualization, also operate on global arrays.
The command used to start TotalView depends on your operating system. For example, the following command starts TotalView on a program invoked using prun using three processes:
Before your program starts parallel execution, a Question dialog launches so you can stop the job to set breakpoints or inspect the program before it begins execution
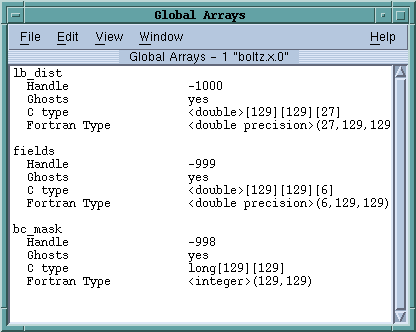
After your program hits a breakpoint, use the Tools > Global Arrays command to begin inspecting your program’s global arrays. TotalView displays the following window.
|
The arrays named in this window are displayed using their C and Fortran type names. Diving on the line that contains the type definition displays Variable Windows that contain information about that array.
After TotalView displays this information, you can use other standard commands and operations on the array. For example, you can use the slice and filter operations and the commands that visualize, obtain statistics, and show the nodes from which the data was obtained.
If you inadvertently dive on a global array variable from the Process Window, TotalView does not know that it is a component of a global array. If, however, you do dive on the variable, you can cast the variable into a global array using either $ga for a C Language cast or $GA for a Fortran cast.