drocm
Displays information about AMD GPU execution states and enables setting GPU focus
Format
Displays a one-line summary of the current agents in the focus thread.
drocm
Displays detailed information about all active objects in the focus process.
drocm info-all
When set to true, sets the display mode of the focus process to show wavefronts as individual threads (wave-thread mode). When set to false, associates agents with TotalView threads (agent-thread mode). The detailed display is determined by the GPU focus of each TotalView thread.
drocm wave_threads [ true | false ]
Displays detailed information about particular ROCm objects in the job.
drocm info-agent
drocm { info-queue | info-dispatch | info-workgroup | info-wave[front] | info-{lane|workitem} } [ -focus | -active | -inactive ]
Displays the agent ID of the current TotalView thread. Cannot be manually set.
drocm agent
Displays or sets the GPU focus of the focus TotalView thread (this applies primarily to agent-thread mode).
drocm { queue [ <queue-id> ] | dispatch [ <dispatch-id> ] | workgroup [ (x, y, z) ] | wave[front] [ <wave-id> | (x,y, z)/<wave-number> ] | lane [ <lane-id> ] | workitem [ \[Tx,Ty,Tz\] ] }
drocm { focus [ (Bx,By,Bz)\[Tx,Ty,Tz\] ] | hwfocus [ A:Q:D:W/L ] }
Arguments
The information displayed by these arguments depends on the subcommand with which they are used.
-focus
-
drocm { info-queue | info-queues } -focus
Shows only the current focus queue (in agent-thread mode).
-
drocm info-dispatch -focus
Shows only the current focus dispatch (in agent-thread mode).
-
drocm info-workgroup-focus
Shows only the current focus workgroup (in agent-thread mode).
-
drocm { info-wavefront | info-wave } -focus
Shows only the current focus wave (in agent-thread mode).
-
drocm { info-lane | info-workitem } -focus
Shows only the current focus lane (in either mode).
-active
-
drocm { info-queue | info-queues } -active
Shows only queues with active dispatches.
-
drocm info-dispatch-active
Shows only dispatches with active waves.
-
drocm info-workgroup-active
Shows only workgroups with active waves.
-
drocm { info-wavefront | info-wave } -active
Shows only waves with nonzero execution masks.
-
drocm { info-lane | info-workitem } -active
Shows only active lanes.
-inactive
-
drocm { info-queue | info-queues } -inactive
Shows only queues without active dispatches.
-
drocm info-dispatch-inactive
Shows only dispatches without active waves.
-
drocm info-workgroup-inactive
Shows only workgroups without active waves.
-
drocm { info-wavefront | info-wave } -inactive
Shows only waves with zero execution masks.
-
drocm { info-lane | info-workitem } -inactive
Shows only inactive lanes.
The following arguments are used with commands to display or set the GPU focus of the focus TotalView thread (applies primarily to agent-thread mode).
queue-id
In agent-thread mode, this sets the focus queue.
dispatch-id
In agent-thread mode, with a numeric argument, possibly with '+' or '-' modifiers (as discussed in the hwfocus description), this sets the focus dispatch. If a full hardware focus string is provided this sets the focus similarly to the hwfocus subcommand.
(x, y, z)
Either the thread or the block x, y, z indices, depending on the command. Include the parentheses.
(Bx, By, Bz)
The x, y, z block indices. Include the parentheses.
(Tx, Ty, Tz)
The x, y, z thread indices. Include the parentheses.
A:Q:D:W/L
The coordinates defining the physical space of the hardware:
A: Agent ID
Q: Queue ID
D: Dispatch ID
W: Wavefront ID
L: Lane index
wave-id
The wavefront ID, i.e., the index of the wavefront of the kernel.
lane-id
The workitem index.
Description
ROCm programs use one or more AMD GPU "agents". Each agent is associated with a GPU, which in turn contains multiple compute units, each of which can run many GPU threads of execution, or "work items".
The individual work items of the job are grouped together into "wavefronts" (or "waves"). Each wavefront typically contains 64 workitems. The workitems in a wave usually execute the same instructions at the same time, and all workitems in a wave are normally in the same state at the same time (running or stopped). For example, when a workitem encounters a breakpoint, the entire wave stops.
An individual workitem within a wave is referred to as a "lane" within the wave. The "index" of a lane within the wave is between 0 and 63.
In addition to the wavefronts, each wave is contained in a dispatch, and the dispatches are grouped together into queues. The agents, queues, dispatches, and waves are referred to by their IDs. The "hardware coordinates" of a particular workitem are its agent, queue, dispatch, and wave IDs, along with the workitem's lane index within the wave. They're written as Agent:Queue:Dispatch:Wave/Lane. For example, agent 2, queue 3, dispatch 1, wave 397, and lane index 13 would be written 2:3:1:397/13.
Each workitem also has "logical coordinates", which are the 3 dimensional coordinates of its workgroup within the grid, along with the 3 dimensional coordinates of the workitem within the workgroup.
TotalView can either associate a debugger thread with each agent in the process ("agent-thread mode"), or it can associate a debugger thread with each wavefront ("wave-thread mode"). The mode is controlled by the command drocm wave_threads [true|false], as mentioned above.
In either mode, the drocm command allows displaying the device status for the agents, queues, dispatches, workgroups, and lanes of the devices used by the code.
Wave-Thread Mode
In wave-thread mode, each TotalView thread represents one wavefront.
The CPU threads in the process are given positive debugger IDs, and the GPU wave threads are given negative debugger IDs. Thus, the CPU threads in a typical process might be numbered 1.1 through 1.4, while the wave threads might receive numbers 1.-1 through 1.-745, depending on how many of them there are.
Step operations, thread hold, and breakpoints marked "stop thread" all work as expected in wave-thread mode. Thus, the waves can be controlled individually, or "asynchronously." This can be extremely convenient when debugging a GPU code which uses a limited number of waves at once.
In wave-thread mode, each debugger thread has hardware coordinates which refer to a particular wave. The lane index for a particular thread is variable, but the remaining coordinates (agent, queue, dispatch, and wave) are fixed for that debugger thread.
Agent-Thread Mode
In a wide GPU code it's possible to have many thousands of waves active at the same time. This can be cumbersome to deal with when each wave is treated as a separate debugger thread.
In agent-thread mode, each debugger thread represents a single agent, rather than a single wavefront. Each agent thread is given a negative thread ID. Thus, in a typical ROCm program in agent-thread mode, the CPU threads might be numbered 1.1 through 1.6, while the agent threads might be numbered 1.-1 through 1.-3. In agent-thread mode, there will be one GPU agent thread for each GPU device visible to the process, whether or not the process is actively using the GPU.
Each GPU agent thread has a "GPU focus", which specifies a single wavefront and lane within the GPU agent. The GPU focus for that thread can be set using the subcommands discussed below. The GPU focus can be specified (and reported) using either logical or hardware coordinates.
The GPU focus is distinct from the CLI (CPU-side) focus.
The CLI focus width determines which agent threads are acted on. If the CLI focus width is set to 't' (thread width) then the drocm command will act only on the CLI focus thread. If the focus width is set to process, group, or 'default', the drocm command will act on all AMD GPU agent threads within the CLI focus. Thus, if the CLI focus is set to "p1.<", the drocm command will act on all agent threads in process 1. If it's set to "t1.-3", the drocm command will act only on thread -3 within process 1.
The drocm command allows inspecting and setting the focus coordinates for the agent threads.
Argument/Subcommand Descriptions
info-all
Displays detailed information about all agents, queues, dispatches, wavefronts, and lanes in the focus TotalView threads. Identical wavefronts are condensed in the display to save space and improve readability, and lane information for the individual lanes of each wavefront is not broken out separately, but this may still produce a substantial amount of output.
drocm info-agent, drocm info-agents, drocm info-device
Displays information about the agents in the focus TotalView thread, with one output line per agent.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the device. In wave-thread mode with a process focus width, this field may be omitted, as multiple threads will have the same agent.
Agent: The Agent ID within the process.
SMI: SMI ID of the agent. This is the ID shown in the rocm-smi command, and is the value used when setting ROCM_VISIBLE_DEVICES to restrict a job to a subset of the available devices.
PCI ID: The location of the device on the PCI bus.
State: Active or inactive.
GPUID: The ID of the GPU.
Device: The device type.
Arch: The architecture of the device.
Cores: The number of compute units on the device.
Waves/Max: The number of wavefronts currently on the device and the maximum number of wavefronts that can be active on the device.
Queues: How many queues are currently on the device.
Disps: How many dispatches are currently on the device.
info-queue, info-queues
Displays information about all active queues in the active agents, with one line per queue. In agent-thread mode, the focus queue is indicated with an asterisk.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the queue.
Queue: The Queue ID within the process, as 'Agent:Queue'.
OS ID: The operating system ID for the queue.
Type: The queue type.
Disps: The number of dispatches in the queue (usually 0 or 1).
St: The status of the queue.
Err: The error code of the queue, if it's in an error state.
R: The Packet ID of the next packet to be read from the queue.
W: The Packet ID of the next packet to be written to the queue.
Size: The aggregate size of all packets in the queue.
Address: The location of the queue.
info-dispatch
Displays information about all active dispatches in the current TotalView thread, with one line per dispatch. In agent-thread mode, the focus dispatch is indicated with an asterisk.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the dispatch.
Dispatch: The ID within the process, as 'Agent:Queue:Dispatch'.
Pkt: The ID of the packet which initiated the dispatch.
Grid: The size of the dispatch's 3D grid, in workitems.
Workgroup: The size of a workgroup within the grid, in workitems. This is the size recorded in the dispatch object, but some workgroups may contain fewer workitems.
Wvs: The number of waves in the dispatch.
Fence: The acquire and release fences for the dispatch. A 'B' indicates there's a barrier present.
Kernel Function: The function being executed by the dispatch.
info-workgroup
Displays the workgroups in the current TotalView thread, with one line per workgroup. The focus workgroup is indicated with an asterisk.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the workgroup.
Dispatch: The ID of the dispatch associated with the workgroup.
Workgroup: The coordinates of the workgroup in the grid.
Size: The dimensions of the workgroup, in work items.
Waves: The number of wavefronts in the workgroup.
info-wavefront, info-wave
Displays the wavefronts in the current TotalView thread, with one line per wavefront. The focus wave is indicated with an asterisk.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the wavefront.
Wave: The ID of the wave, as 'Agent:Queue:Dispatch:Wave', using hardware coordinates. The wave coordinates are shown as Bx,By,Bz)/Wnumber, where Bx,By,Bz are the coordinates of the workgroup, and "Wnumber" is the "wave number" within the workgroup. The "wave number" is the index of the wave in the workgroup, and should not be confused with the "wave ID", which is a process-wide unique ID associated with the wave.
Lns: The number of lanes in the wavefront.
Exec: The current execution mask for the wavefront.
S: The state of the wave, as follows:
R: Running
T: Stopped
SS: Stepping
?: Unknown
Res: The stop reason mask for the wave (if it's stopped). Multiple reasons may be given, as "B|SS|..." Possible reasons include the following:
Aper: Aperture violation -- Reference out of bounds
Assert: Assert trap
B: Breakpoint
Debug: Debug trap
Div0: Integer divide by zero
ECC: Unrecoverable ECC error (hardware error)
FP_Denorm: Floating point: denormalized result
FP_Div0: FP divide by zero
FP_Inexact: FP inexact result
FP_Inval: FP invalid operation
FP_Over: FP overflow
FP_Under: FP underflow
Fatal: A fatal error occurred
Ill: Illegal instruction or operation
Mem: Memory violation
SS: Singlestep completed
Trap: Trap
W: Watchpoint
Frame: The function and line number for the active stackframe.
info-workitem, info-lane
Displays the lanes in the focus wavefront, with one line per lane. The focus is indicated with an asterisk.
Fields displayed:
Thread: The TotalView thread associated with the lane
Lane: The ID of the lane using hardware coordinates, as "Agent:Queue:Dispatch:Wave/Lane-index", along with the logical coordinates of the workitem, as "(Bx,By,Bz)[Tx,Ty,Tz]". Bx,By,Bz are the coordinates of the workgroup within the grid and Tx,Ty,Tz are the coordinates of the workitem within the workgroup.
S: The state of the lane. Possible states include the following:
A: Active (its bit is set in the wave's execution mask)
I: Inactive
Res: The stop reason mask, if the lane is active. This is the same as the Res field for the wave.
Frame: The function and line number for the active stackframe.
The following subcommands are intended for use in inspecting and setting the GPU focus. The first two, focus and hwfocus manipulate the entire focus, while the others are for printing or setting particular components of the focus. These are primarily for use in agent-thread mode, since only the lane subcommand can be set on a wave thread.
focus
With no arguments, displays the dispatch ID and the ROCm logical coordinates of the focus workgroup and workitem in the form "(Bx,By,Bz)[Tx,Ty,Tz]". If a further argument is given, in agent-thread mode this changes the GPU focus to the provided coordinates.
If not all coordinates are given, the missing coordinates retain their present values. The following abbreviations to the coordinate string are also accepted (with missing values filled in from the current focus):
(Tx)
(Tx,Ty)
(Tx,Ty,Tz)
(Bx)/(Tx)
(Bx)/(Tx,Ty)
(Bx)/(Tx,Ty,Tz)
(Bx,By)/(Tx)
(Bx,By)/(Tx,Ty)
(Bx,By,Bz)/(Tx)
(Bx,By,Bz)/(Tx,Ty)
With no arguments, displays the ROCm hardware coordinates of the focus workgroup and workitem in the form "Agent-ID:Queue-ID:Dispatch-ID:Wavefront-ID:Lane-index". If a coordinate argument is given, this changes the focus to the specified values. This can be used in either wave or agent-thread mode, but in wave-thread mode, only the focus lane can be changed.
Attempting to set the focus to values that aren't valid will either result in an error, or will set the focus to a valid value which is "close" to the provided values. Changing the queue or dispatch value will always also result in a change to the focus wave, because the wavefront ID values are unique process-wide, and so the same focus wave ID cannot appear in more than one queue or dispatch.
In agent-thread mode, the agent is bound to the TotalView thread ID. That binding is fixed. To change the agent on which you're focused, you need to change the TotalView thread in the general (CPU-side) focus, using the 'dfocus' command.
If some of the values are left out, they will be left unchanged (if possible), or legal values "close" the provided values will be filled in. If the string provided contains a '/', the value before the slash will be the wave ID. If there is no '/' then the first value in the string will be the agent, and any missing values will be filled in from the current focus on the right end of the string. Any missing values will be left unchanged (if possible). Note that in the following examples, the value of "A", if it is provided, must match the current agent for the agent thread; to view a different agent you must focus on the TotalView thread which is bound to that agent. Thus, the following string formats are accepted, where "A" is agent (and, if provided, must match the current agent), "Q" is queue, "D" is dispatch, "W" is wavefront ID, and "L" is lane index:

Imprecise values
If a new focus value is not valid, TotalView tries to find a "nearby" value which is valid. It searches both up and down for the new value, and uses the closest one found.
Finding a nearby Lane
When searching for a valid lane, the search does not extend outside the current wave. If there's no match within the current wave, an error is returned.
Finding a Nearby Queue, Dispatch, or Wave
The focus string is interpreted from left to right: first the Queue, then the Dispatch, and then Wave. The first focus component which is given a new value is checked, and if the new value is not valid, the search for a "nearby" value extends across all values for that component within the agent.
If the Dispatch is being set, and the closest valid value which is found for the Dispatch belongs to a different Queue from the current focus queue, the Queue will be changed to the one which includes the Dispatch which was found.
Once a new value is set for a component, values for subsequent components are constrained to lie within the previously selected focus objects. Thus, if you set the focus to ":2::17", the Queue will be set to 2 (or the closest match), the Dispatch will, if necessary, be changed to a dispatch within Queue 2, and the Wave (which you've asked to set to 17) will be changed, if necessary, to a wave within the newly selected dispatch.
Relative Values: '+' and '-'
If a '+' or '-' is included in the focus string, then the new value is set relative to the old value. Thus, "+3/" will try to increment the wave ID by 3, and leave everything else unchanged.
If a '+' or '-' is given without a number, it's treated as though the number was 1. Thus, "+/" tries to step to the next wave. "/-" tries to step to the next lower numbered lane.
If it's necessary to search for a valid value with a relative value, if the sign on value was '+', then TotalView will search up from the new value. If the sign was '-', then the search for a valid value will go down. If no valid value at or above the new value is found, and the direction was '+', the highest valid value which was found will be used. If the search was downward, the lowest valid value which was found will be used.
Controlling the Direction of Search: Postfix '+' and '-'
If you want to give a number for a focus component, and you also want to specify the direction to look if the value given is not valid, you can append a '+' or '-' to the number. Thus, "27-/" means 'Focus on wave 27, and if there is no wave 27, look *down* to find the closest match".
Forcing an Exact Match: '='
If you don't want any searching, you can prepend a '=' to the value. Thus, "::=7" means "Set the Dispatch to 7, or fail." No searching will be done.
To force an old value to be retained you can use a bare '='. Thus, ":3:=:" means "Set the queue to 3, and leave the Dispatch ID unchanged. If that can't be done, return
an error".
The '=' is intended for use in scripts. It's unlikely to be of much use interactively.
The remaining subcommands are intended for use in manipulating particular components of the focus.
agent
Show the agent focus. Displays the ID of the agent associated with the current TotalView thread.
You cannot provide a value to the 'agent' argument, because the agent cannot be set this way (as discussed in the hwfocus section, above).
queue
Show or (in agent-thread mode) set the focus queue. Displays the ID of the queue associated with the focus wavefront and workitem.
With a numeric argument, possibly with '+' or '-' modifiers (as discussed under hwfocus above), this sets the focus queue.
If a full hardware focus string is provided this sets the focus similarly to the hwfocus subcommand.
dispatch
Show or (in agent-thread mode) set the focus dispatch. Displays the ID of the dispatch associated with the focus wavefront and workitem.
With a numeric argument, possibly with '+' or '-' modifiers (as discussed under hwfocus above), this sets the focus dispatch.
If a full hardware focus string is provided this sets the focus similarly to the hwfocus subcommand.
workgroup
With no arguments, shows the dispatch ID and the coordinates of the current ROCm workgroup. With a coordinate argument of the form (Bx,By,Bz), this changes the ROCm focus of the GPU agent thread to that workgroup. Components to the right (By and Bz, or Bz) may be omitted, and are left unchanged.
wavefront
Show or (in agent-thread mode) set the focus wave. With no arguments, shows the ID and coordinates of the currently selected ROCm wavefront.
With a single numeric argument, changes the ROCm focus of the GPU agent thread to the wavefront with that ID. Note that the wavefront IDs are unique process-wide.
With an argument of the form "(x,y,z)/number", this changes the focus to wavefront number "number" in workgroup "(x,y,z)". The wavefronts in each workgroup are numbered consecutively starting at 0. The "wave number", which is the index of the wave in the workgroup, should not be confused with the "wave ID", which is a process-wide unique ID associated with the wave.
If a full hardware focus string is provided this sets the focus similarly to the hwfocus subcommand.
workitem
With no arguments, shows the coordinates of the focus ROCm workitem.
With a coordinate argument of the form [Tx,Ty,Tz], in agent-thread mode, changes the ROCm focus of the GPU agent thread to that workitem. Note that these are the workitem's coordinates within the workgroup; the workgroup is left unchanged. Parameters to the right (Ty and Tz, or Tz) may be omitted, and are left unchanged.
If a full logical focus string is provided this sets the block and workitem, similarly to the focus subcommand.
lane
With no arguments, shows the current ROCm lane index within the current wavefront.
With a numeric argument changes the ROCm lane focus to that lane (in either agent or wave-thread mode). Note that the focus wavefront is left unchanged by this, and the provided lane index must be valid within the current wave.
Command Alias
|
Alias |
Definition |
Description |
|
rocm |
drocm |
Displays device information, or displays/sets the focus of the ROCm thread. |
Examples
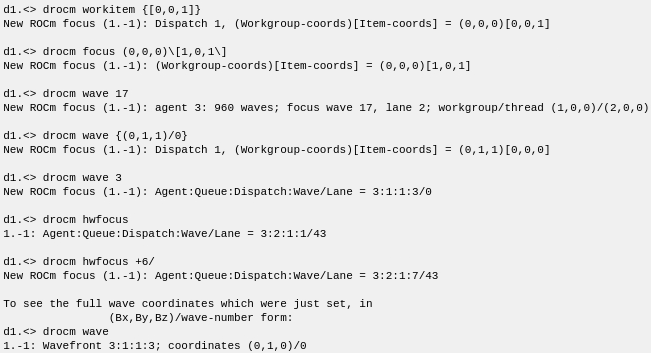
Displaying information in agent-thread mode
The following example displays device information in agent-thread mode. Notice that the example starts by focusing on a ROCm debugger thread.

The following example are in agent-thread mode. TotalView thread 1.-1 represents one agent. Details to be displayed controlled by the GPU focus of thread 1.-1.
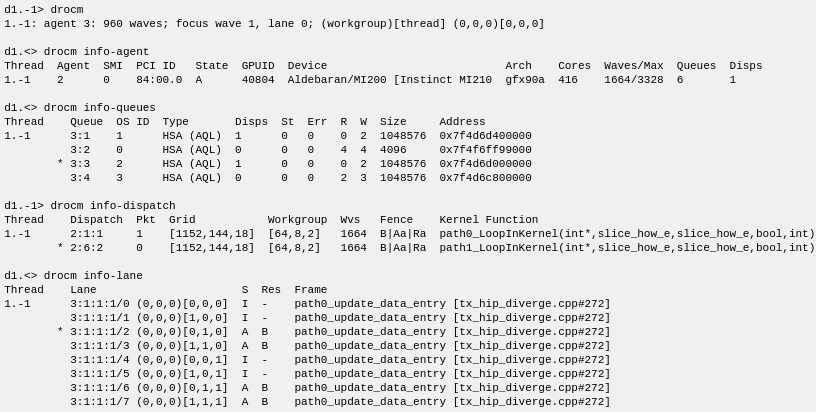
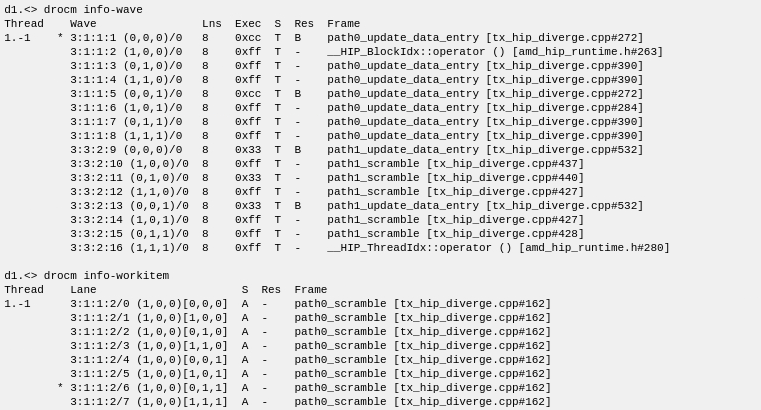

Displaying information in wave-thread mode
The following example switches debugging to wave-thread mode.

Note that there were over 3000 lines of output after switching the mode. This is because there were over 3000 active wavefronts, and with each wavefront bound to a separate TotalView thread, there were necessarily over 3000 TotalView threads active.
The display of active queues and dispatches is much the same as in agent-thread mode.
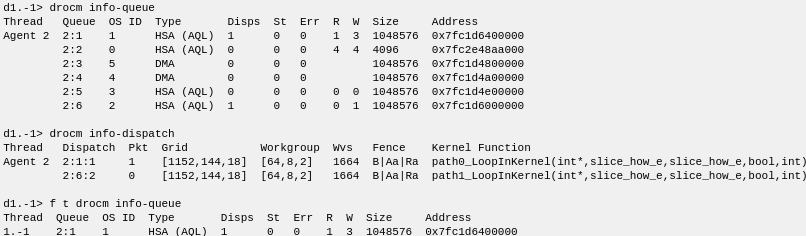
If a thread width is specified, information returns on just the single wave-thread on which the focus is set.
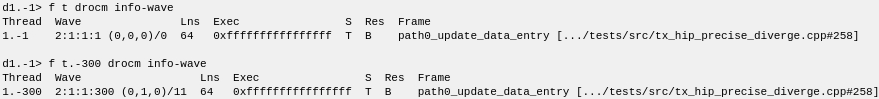
Restarting with a much smaller set of active waves (to keep the output compact) shows some additional things you can do with wave-thread mode.

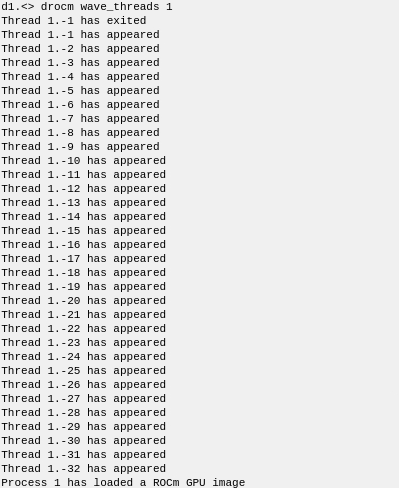
When you switch to wave threads mode, 32 wave threads appear (one for each wavefront).
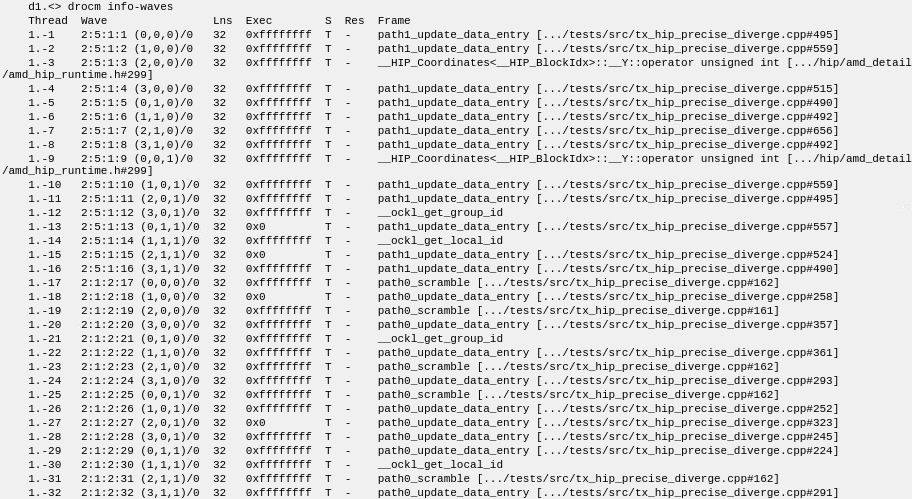
Requesting information on the waves show 32 TotalView threads, each bound to a different wavefront, with the execution points of all of them scattered around in the code.
If you plant some stop-thread breakpoints, they'll be planted everywhere that they make sense (in the GPU code as well as the CPU code).
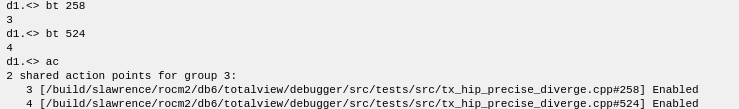
And when you run the process, the following result is returned.
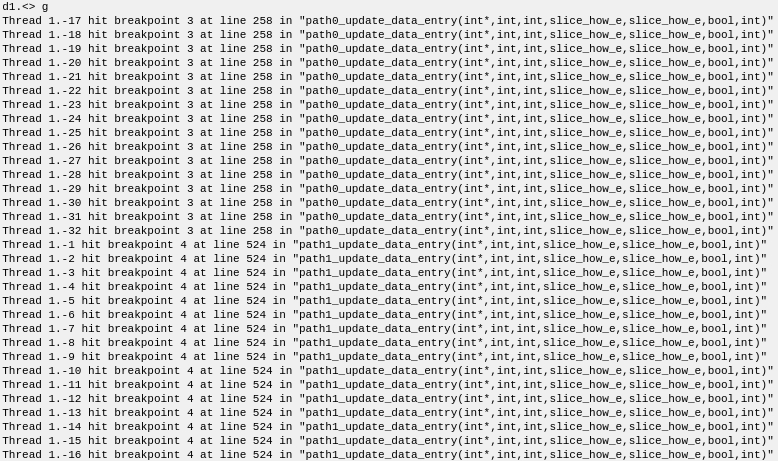
The waves all ran until each of them hit a breakpoint. If you ask for info-wave now, you'll see that they're all at one of the two breakpoint locations.
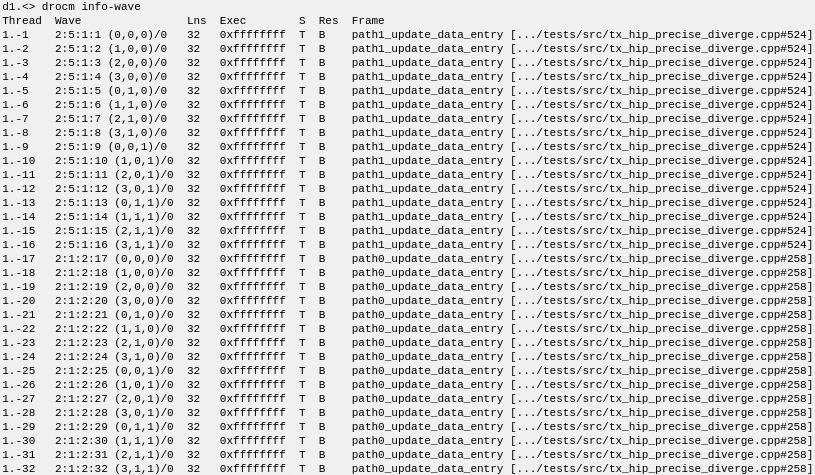
There are two dispatches in use.

Restricting the display to just focus, active, or inactive objects
For the following examples, debugging is set back to agent-thread mode.
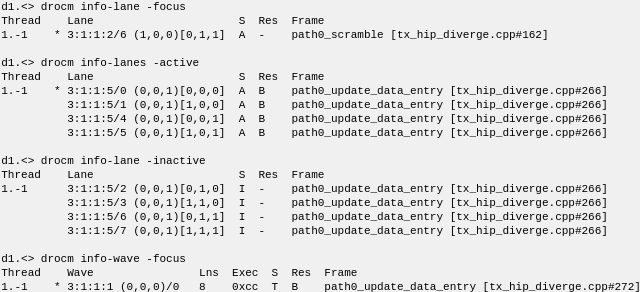
Displaying the focus

Changing the focus lane in either mode

Changing the focus in agent-thread mode